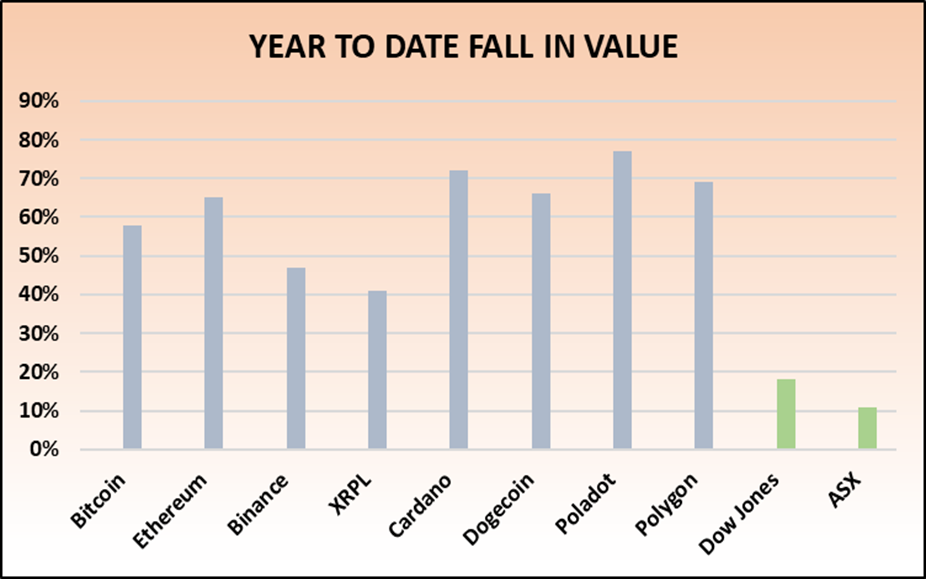
The slingshot effect
As a property market analyst, I’m always looking for tips and tricks that can help investors find areas with growth potential before the growth actually occurs. So what if I told you that there’s a way to easily find areas that have growth potential even while prices are falling? Well there is, and it’s called the slingshot effect.

Have you noticed that when you fire a slingshot, you have to pull the payload down so that it will shoot up?
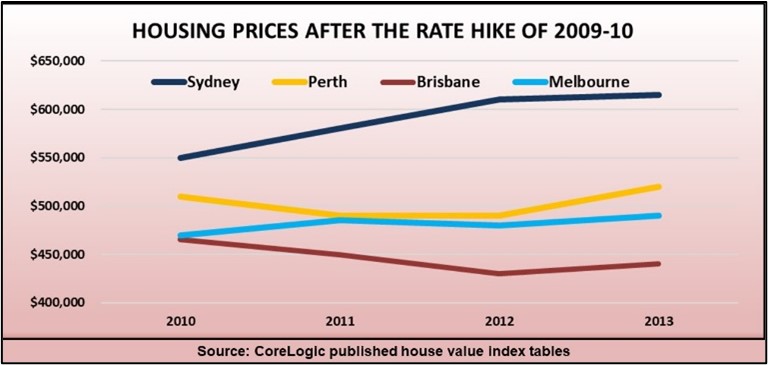
The same thing takes place in property markets when growth is about to return, because astute buyers move in and buy up the low priced bargains first, which actually pulls prices down until the cheapies are all gone.
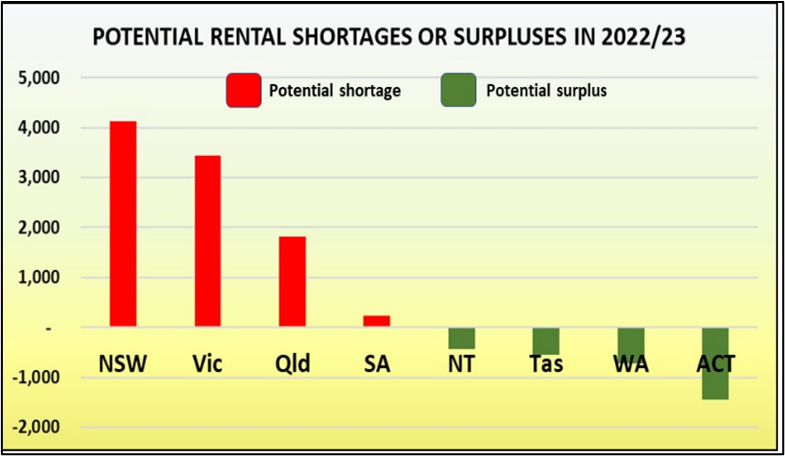
The median price measures the middle point of all sales, so even if sales are rising, the median sale price starts to fall because the bargains get snapped up first.
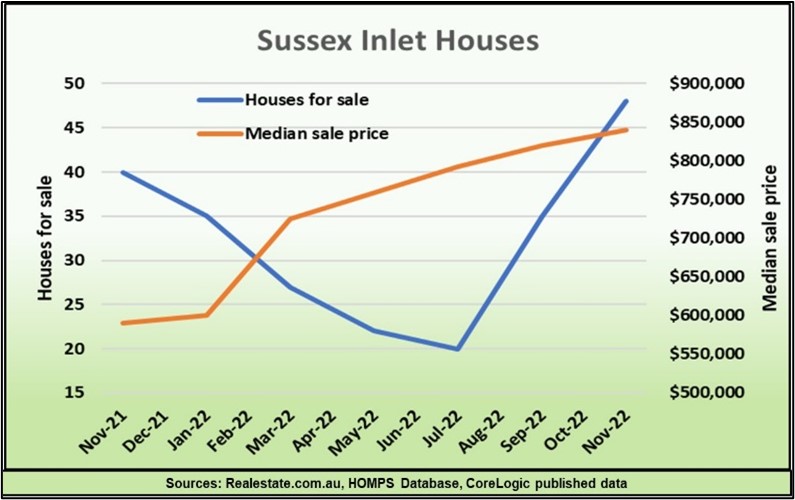
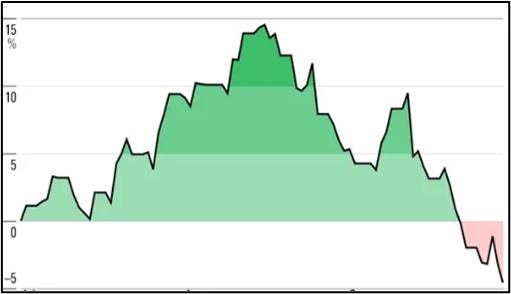
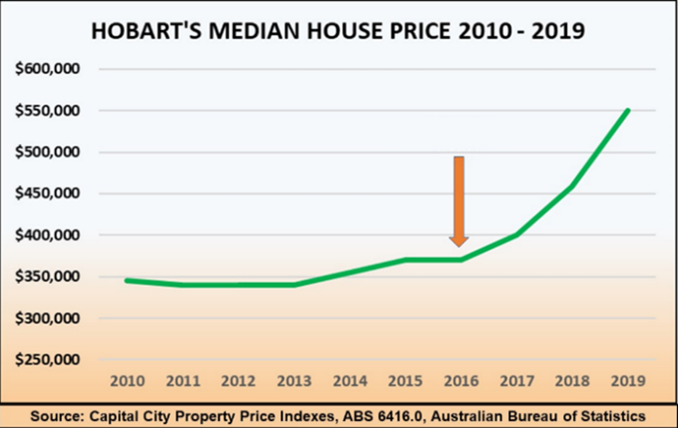
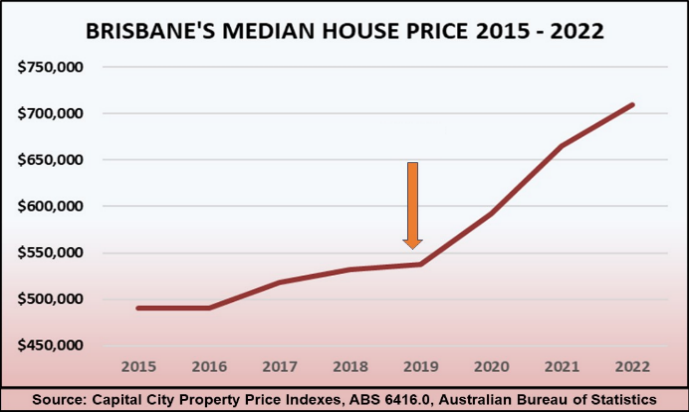
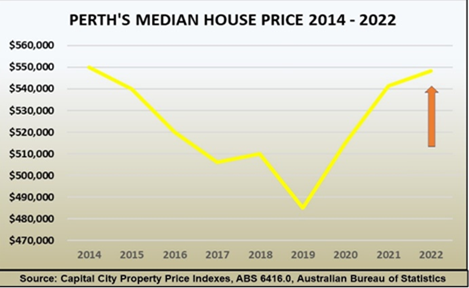
This table shows you how the median (in blue) is hiding the fact that buyer demand is actually growing and prices will soon rise.
Prices start to shoot up, like a slingshot being fired, once all the cheaper listings are gone. Buyers now must compete for dearer properties, and growth quickly returns.
The slingshot effect happens whenever market conditions change, motivating potential buyers to act after many months or even years of stagnation or price falls. It occurs purely because the bargain properties get sold first, so that median prices can’t rise until they are all gone.
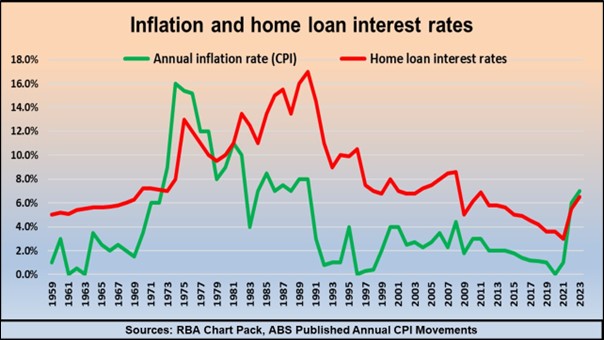
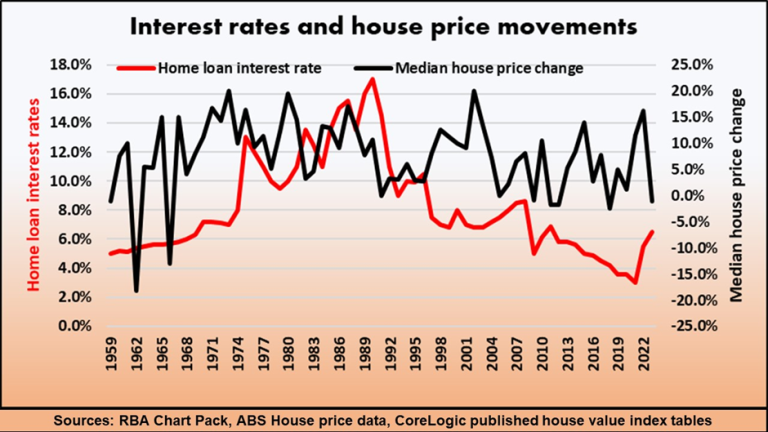
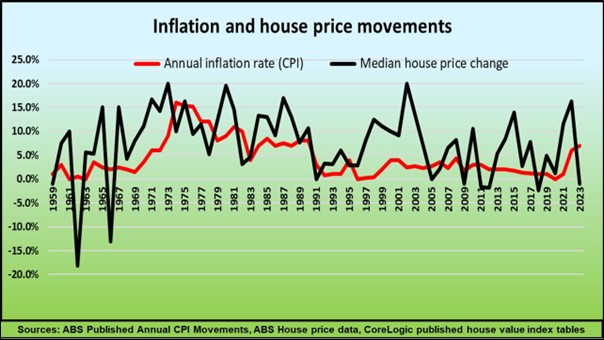
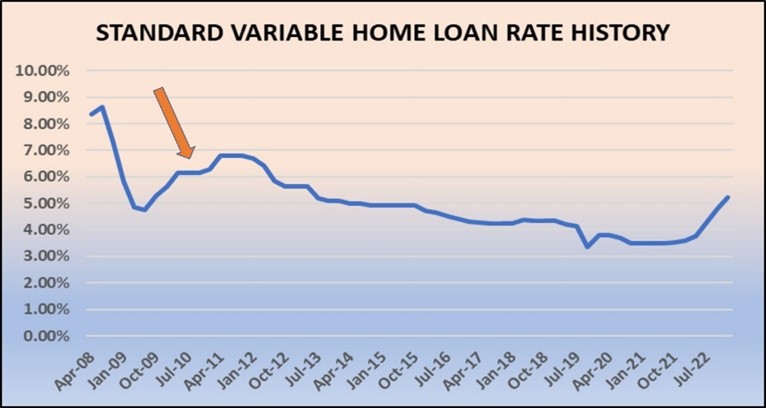
This graph illustrates how the slingshot effect works, showing that it took many months after interest rates dropped in 2020 before house prices boomed in 2021.
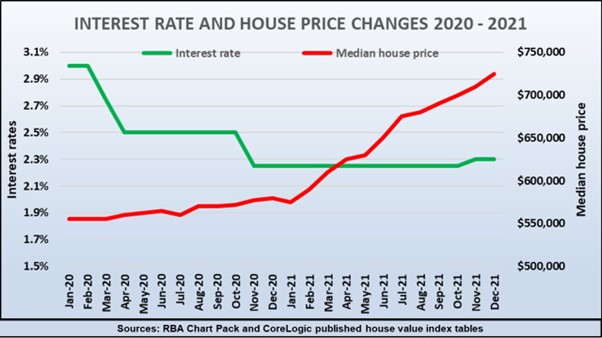
Even though the number of buyers rapidly grew during 2020, there were sufficient stocks of properties for sale to soak up the demand, and there was no significant rise in prices. By late 2020, however, the turning point was reached as the number of aspiring home buyers outpaced the number properties listed for sale and as all the cheapies were gone, prices suddenly boomed.
This time around exactly the same dynamics will unfold and clever investors can use the slingshot effect to find bargains in suburbs just before prices shoot upwards. Watch for locations where the median house price has been falling, but sales are trending up and the number of properties listed for sale is steadily declining.
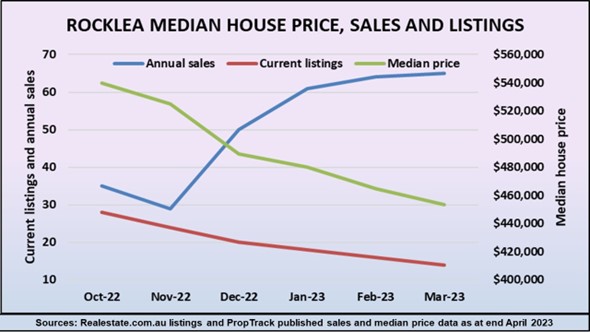
For example, the median house price in the inner Brisbane suburb of Rocklea has fallen by around $100,000 since last October, but the number of sales has doubled over the same time. This doesn’t make any sense, unless you realise that it’s the slingshot effect at work, and once all the cheapies are gone, prices will boom.
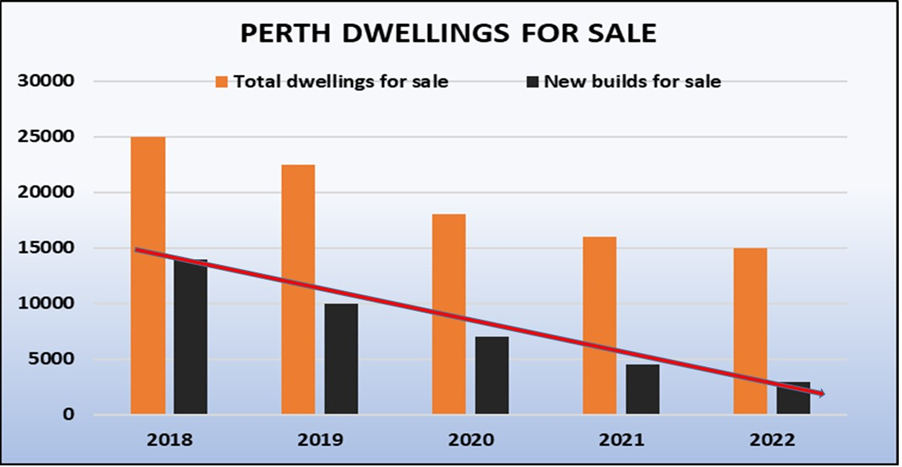
To confirm that this is happening, we can see that the number of listings in Rocklea has nearly halved since last October, and that there are very few low-priced bargains left for sale. It’s only a matter of months before prices soar again.
That’s how the slingshot effect works. It enables savvy buyers to snap up bargains from vendors who are unaware that the market has changed.